
1. College of Fisheries, Guangdong Ocean University, Zhanjiang, China
2. College of Life Sciences, Hubei Normal University, Huangshi, China
3. Donghu Experimental Station of Lake Ecosystems, State Key Laboratory of Freshwater Ecology and Biotechnology, Institute of Hydrobiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Wuhan, China
4. College of Advanced Agricultural Sciences, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China
5. ISEM, Université de Montpellier, CNRS, IRD, EPHE, Montpellier, France
Chuanbo Guo, Institute of Hydrobiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Wuhan, Hubei 430072, China.
Email:guocb@ihb.ac.cn
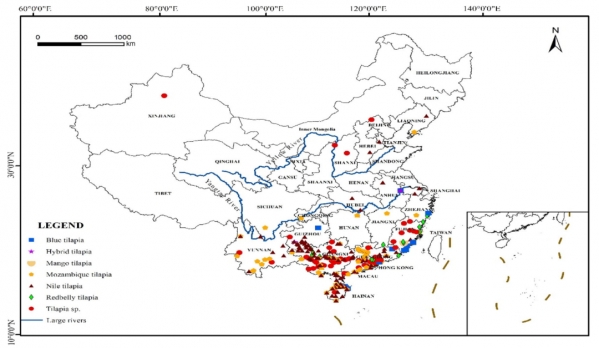
罗非鱼在全国范围内的分布
摘要
外来物种的引进和养殖是全球水产养殖业发展的重要环节,其中,罗非鱼是全球引进最广泛的物种之一,而中国则是罗非鱼的最大生产国与消费国。外来的罗非鱼为中国的生态系统服务创造巨大的经济价值的同时,也对本土鱼类多样性、生态系统和渔业可持续发展造成了潜在威胁。然而,我们对外来物种的入侵途径、渔业经济价值和生态效应等诸多方面不甚了解。本文基于系统的文献回顾和实地调研,全面介绍了罗非鱼在中国不同水生生境的引进情况以及其在水产养殖业发展中的重要作用,强调了经济效益。此外,本文还立足于全球过往的经验教训,总结了罗非鱼入侵对生态系统的潜在影响,为中国和世界各国提供宝贵的指导和管理建议。根据目前的趋势,中国引进罗非鱼的数量和频率仍将持续增加,因此对环境造成破坏的可能性也越来越大。然而,由于罗非鱼养殖的高额利润,进一步的引进是无可避免的。因此,本文进一步讨论了不同的养殖管理策略和措施,从而实现更可持续和生态系统友好的水产养殖,减少对生态系统造成的风险和负面影响的同时保持经济效益。
关键词
水生生态系统,生物入侵,保护,生态风险,水产养殖可持续发展,罗非鱼
The introduction and use of non-native species in aquaculture have played a central role in the development of this economic sector worldwide. Tilapia is one of the most widely introduced species in the world, and China has become the largest producer and consumer of tilapia. While non-native tilapia in China support provisioning ecosystem services of substantial economic value, the invasion also poses potential threats to native fish diversity, ecosystems and ultimately the sustainable fisheries development. However, knowledge regarding the invading pathway, aquaculture development, economic benefits and the ecological impacts of such important non-native species is still limited, especially in China. Based on thorough literature review as well as field surveys, this paper has comprehensively presented the introduction of tilapia species across a range of aquatic habitats and its role in the aquaculture industry growth, emphasising the economic benefits in China. In addition, we also synthesised the potential negative ecological impacts caused by tilapia invasion with global evidences, which will provide excellent lessons and management recommendations for China and other countries worldwide. Future trends tend to indicate an increase in the number and frequency of tilapia's introduction in China, with an increasing likelihood of environmental impacts. However, it is apparent that the aquaculture of non-native tilapias is a highly profitable activity in China which makes the introductions inevitable, therefore, alternative management strategies and implications are further discussed to seek to achieve more sustainable and ecosystem-friendly aquaculture, reduce the risks and negative impacts on ecosystems while still maintaining the economic benefits.
keywords
aquatic ecosystem, biological invasion, conservation, ecological risk, sustainable aquaculturedevelopment, tilapia